Insights: Permanent Carbon Removal RFP: Phase 1 concludes with strong applicant pool
Reading Time: 8min

At Planet2050, our core mission is to accelerate the global transition to net zero by financing and scaling high-quality, verifiable carbon removal and reduction projects. We recognize both the immense potential, and the considerable challenges, of bringing innovative climate solutions to life.
We have stepped on to the journey towards transformational climate action through our Request for Proposals (RFP) for Permanent Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) launched on June 24, 2025, inviting project developers around the world to tell us about their ambitions, projects and capital requirements. This previous post details why and how we are doing it.
With the close of the First RFP Phase on July 22nd, we are excited to share some early insights.
We hope this snapshot offers a compelling look at the burgeoning and much-needed ecosystem of CDR climate changemarkers.
310 project applications
We are very pleased with the overwhelming response from the carbon removal ecosystem, having received 310 project submissions that align with the scope of our Permanent CDR RFP.
This robust engagement underscores the growing vitality and innovation within the sector, as well as the critical need for pre-financing options for climate action from start to scale.
We are thankful to all partners and market participants who helped share the message and thereby bring the Planet2050’s vision closer to reality: Puro.Earth, Isometric, Rainbow, Carbon Standard International, German Biochar e.V., IBI, Quantum, Cula, Offstream, Carbonfuture, CDR.Fyi, BlueLayer, Carbon Pulse, Airminers .
Our team is currently reviewing the submissions and short-listing the organizations who will participate in the second round of the RFP starting in August.
In line with our principles on transparency and open practices, we are excited to share an initial analysis of RFP data, highlighting key trends and characteristics of the accelerating carbon removal landscape.
Key Data Analyses from RFP Submissions
Project Submissions Overview
We received a strong response, with 310 project applications from 274 organizations, falling within the defined scope of our Permanent Carbon Dioxide Removal (CDR) RFP.
Dominant CDR Methodologies
A vast majority of project applicants, 65%, submitted projects utilizing biochar as their durable Carbon Removal method. This confirms biochar as a highly mature, replicable, and sought-after solution, not only for carbon removal at scale but also for addressing localized issues such as biomass decomposition, field burnings, forest fires, soil remediation, and enhancing crop resilience.

Additionally, Biomass Burial is emerging as an increasingly popular methodology, evidenced by a surprisingly high number of applications in this area.
Applicant Organization Maturity
While the CDR space has seen significant emergence of climate-tech startups around 2021-2022, our applicant pool reveals a diverse age profile.
Nearly a quarter of the submitted projects originate from organizations established within the last 18 months, reflecting rapid innovation.

Interestingly, established players are joining the rally in the CDR space. 32% of applications came from organizations launched more than five years ago (11 of which had been incorporated before 2000), indicating a growing engagement from more traditional sectors such as forestry, construction, timber, and energy, who are now initiating CDR projects.
Geographical Reach of Submissions
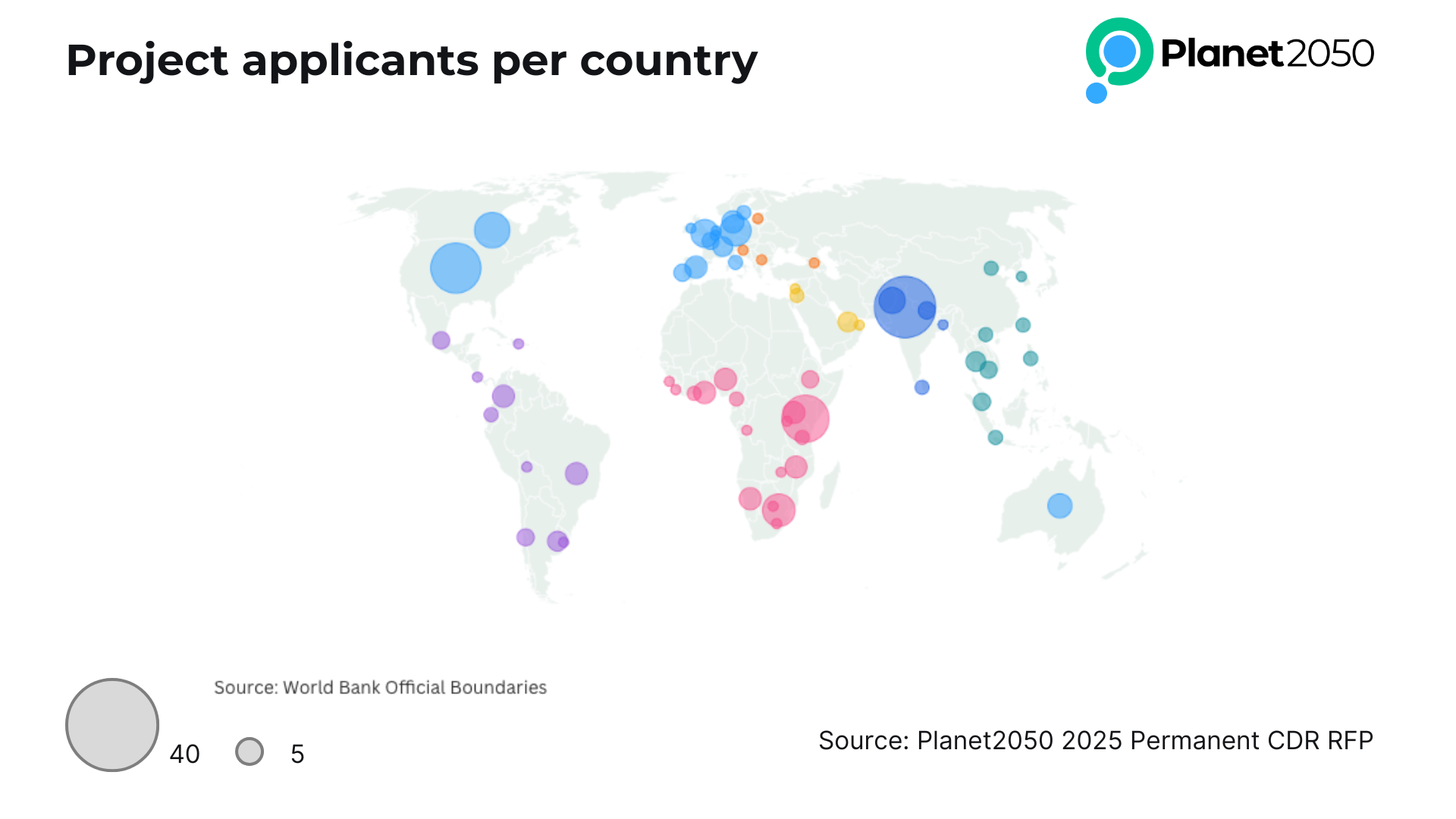
As regards the geographical reach, the RFP garnered global interest, with projects being designed or implemented in 66 different countries.
48 submitted projects are based in Europe.
34% applicants are developing projects in the Global South, versus a majority (66%) in the Global North.

Leading the international submissions were projects located in India (39 projects, 14%), followed by the USA (26 projects, 9.4%), and Kenya (23 projects, 8.3%). Other significant submitting countries include Canada, South Africa, Germany, the UK, Pakistan, Australia, Brazil, Colombia, Denmark, and Ghana.
Altogether, an impressive 53% of project submitted are based in Africa or Asia.
An interesting insight is that 21 projects stem from US-headquartered entities operating globally, highlighting the trend for "cross-border" CDR project development.
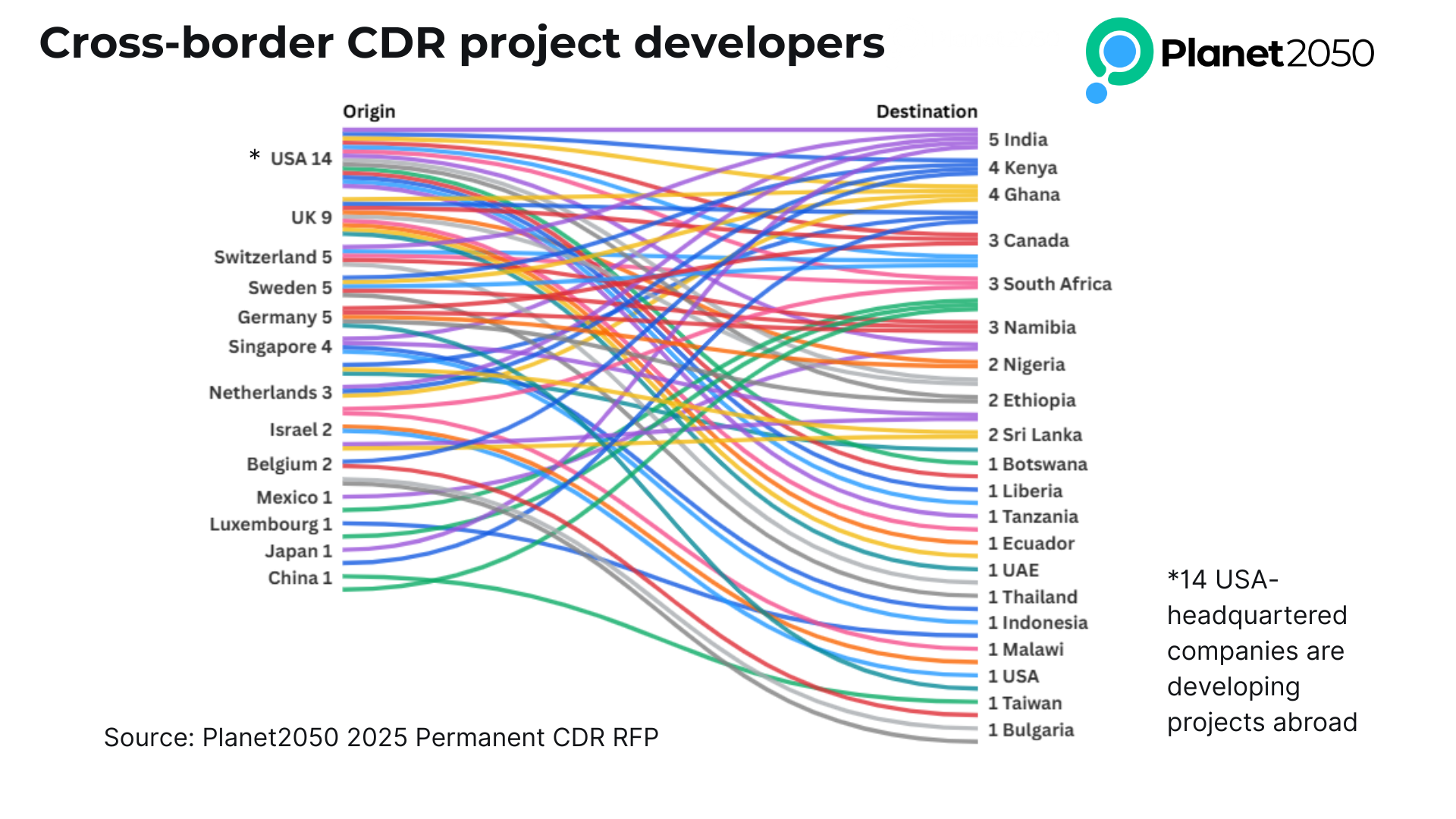
Similarly, a number of Swiss, German and Sweden-incorporated organizations are submitting projects located in countries abroad.
Project Development Stage Distribution
The submitted projects exhibit a relatively even distribution across various development stages, from early-stage projects (47%) focused on feasibility studies, and Project Design Documents (PDD), to later-stage initiatives (53%) pending registration/ certification or already in pre- or post-issuance phases.

Projects that have already achieved post-issuance status typically seek working capital or new funding for expansion and scale-up.
Carbon Standards Adoption
A significant majority of projects either have, or plan to obtain, certification through leading CDR-focused standards:
Puro.earth is the most frequently cited (39.3%)
Isometric (15.3%)
CSI (15.3%)
Rainbow (7.9%)

Reflecting the evolving standards landscape, 21 applicants indicated they are considering between two or more standard options, and 11 organizations are already working with multiple standards across their portfolio of projects.
Verra, the leading Voluntary Carbon Market standard has released methodologies and initiatives in the past years, for example:
Biochar methodology (VM0044 Biochar Utilization in Soil and Non-Soil Applications, v1.2) updated in June 2025
Enhanced Weathering and Mineralization Advisory Group (EWM AG) in place with methodology under development
VM0049 Carbon Capture and Storage, v1.0 active since June 2024
Consequently, 15 project developers have selected Verra as standard for their project activities and a dozen are considering it as part of several options.
Two applicants are following ISO emissions accounting approach, and two others have mentioned Gold Standard as their selected standard.
Gold Standard has just published in July 2025 its Engineered Removals Requirements, which may encourage more project development to apply with them in the near future.
First Credit Issuance Timeline
The pathway to credit issuance varies, with promising signs of near-term supply. Almost a third of project applicants have either already issued their first credits or anticipate their initial issuance within the next six months.

For the remaining projects, the majority target their first issuance in 2026. Projects focused on emerging, large-scale Direct Air Capture (DAC), Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS), or Direct Ocean Capture (DOC) technologies typically project longer timelines, requiring three to five years before their first planned CDR issuance.
Diversified Revenue Streams
Beyond CDR credits, a strong majority of projects (65%) are strategically planning for multiple revenue sources.
These commonly include revenues derived from sustainable materials (e.g., biochar, construction materials), energy (e.g., heat, electricity), other valuable products (e.g., bio-oil), or through decarbonization and insetting services.
This strong trend towards multi-revenue streams highlights a sophisticated and resilient approach within the carbon removal sector.
By integrating various income sources, projects significantly enhance their financial viability and appeal to investors.
This strategic diversification not only strengthens project resilience but also accelerates the transition towards a more circular and sustainable economy, where climate solutions are inherently linked to valuable products and services.
Financing Preferences
Planet2050 is structuring a range of financing options, including equity, forward, and streaming agreements.
Applicants generally expressed interest in multiple financing sources, recognizing the blended capital needs of CDR projects (we talked about it here).
Pre-sales of carbon credits remain the most popular option. Approximately 20% of applicants are considering equity financing. Grants are particularly appealing for technology-focused project developers, not only for their non-dilutive nature but also for their crucial role in de-risking and maturing nascent technologies.
Forecasted Lifetime Carbon Dioxide Removals (tCO2e) by Project
Based on the declared information by 216 applicants, the number of projects categorized by their forecast lifetime Carbon Dioxide Removals (tCO2e) is as follows:
<10k: 37 projects*
10-100k: 88 projects
100k-1M: 62 projects
>1M: 29 projects
*Explainer: 37 projects forecast a lifetime carbon removal amount below 10,000 tCO2e.
Important caveat: this data represents raw, self-declared information from the initial screening stage and like other data points has not yet undergone validation.
What’s next?
Projects are going through an initial assessment following eligibility and assessment criteria which we had presented in the RFP Guidelines.
Shortlisted projects will advance to the second phase of the RFP beginning in August, with selections expected in September. We anticipate partnership and pre-financing to start in Q4 2025.
Upfront for a Net Zero Planet
We are excited by the prospect of partnering with pioneering carbon removal projects to unlock capital, provide strategic support, de-risk development, and amplify their global impact.
The journey to a net-zero world requires bold action, and the overwhelming response to this RFP reinforces our belief that the CDR sector is ready to deliver.
We extend our sincere thanks once again to all applicants.
We look forward to scaling climate action with you.